Bacteria Domain Definition Biology

4 molecular biology a part of a.
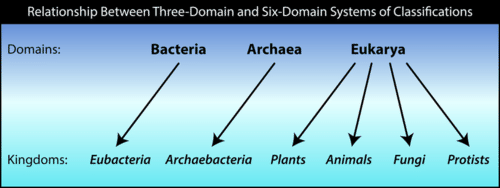
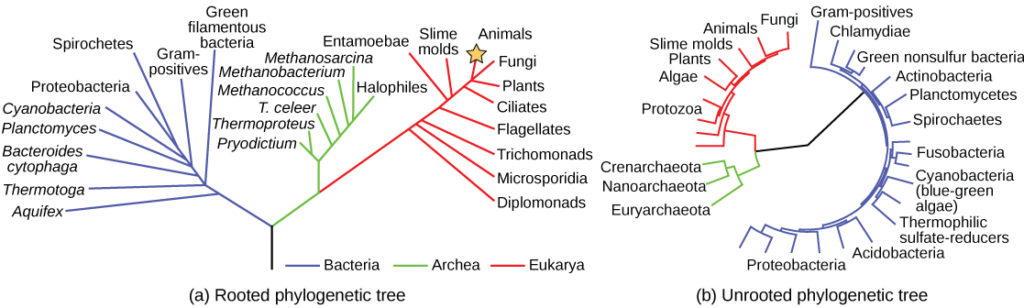
Bacteria domain definition biology. Et le domaine eukaryota ou eucarya. The other two domains of life are archaea members of which are also single celled organisms with prokaryotic cells and eukaryota. Cyanobacteria and mycoplasmas are two examples of bacteria.
Most bacterial species are heterotrophic. D autres modèles ont été proposés parmi lesquels. Ces taxons comportent des différences fondamentales dans leurs génomes.
These organisms are generally feared because some are pathogenic and capable of causing disease. Les unicontes et bicontes sont des sous domaines des eucaryotes 6. Bacteria with a capital b refers to the domain bacteria one of the three domains of life.
However bacteria are essential to life as some are part of the human microbiota. Eubacteria can be found almost everywhere and kill thousands upon thousands of people each year but also serve as antibiotics producers and food digesters in our stomachs. Bacteria are classified under the bacteria domain.
Modèle à deux empires. The bacteria eubacteria bacteria also known as eubacteria or true bacteria are prokaryotic cells that are common in human daily life encounter many more times than the archaebacteria. Each domain contains a collection of organisms with similar properties and evolutionary histories as scientists have organized them.
Bacteria even though bacteria are prokaryotic cells just like archaea their membranes are made of phospholipid bilayers. They characteristically do not have ether linkages like archaea and they are grouped into a different category and hence a different domain. 3 anatomy a place in or a division of the body or a part of the body as abdominal region.