Domain Bacteria Biology Definition

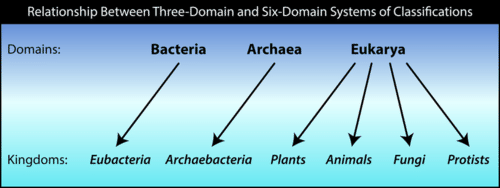
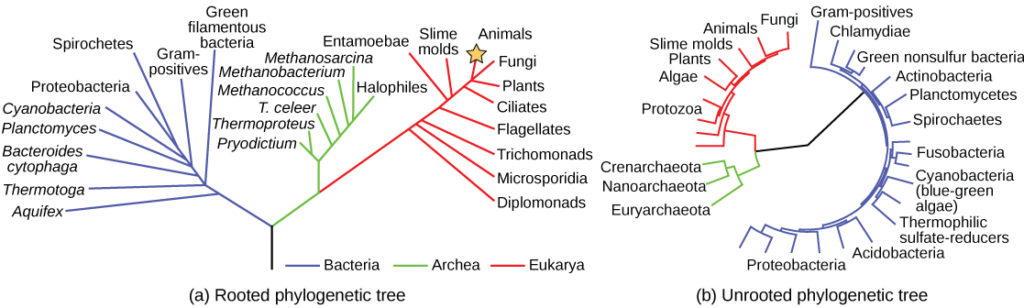
There are currently 3 agreed groups at this level the archaea domain bacteria domain and eukarya domain.
Domain bacteria biology definition. Since eubacteria is so common it comprises one of the three domains. Two of the three domains bacteria and archaea are prokaryotic. Supplement eukarya or eukaryota is one in the three domain system of biological classification introduced by carl woese in 1990.
In the food industry bacteria are used to prepare products such as cheeses fermented dairy products sauerkraut and pickles. In other industries bacteria are used to produce antibiotics chemicals dyes numerous vitamins and enzymes and a number of insecticides. Archaea in the largest biology dictionary online.
It should be noted that while the three domain system is widely accepted and taught it has been contested by a number of scientists. The other two are archaea and bacteria. All types of bacteria fall under this title except for archaebacteria.
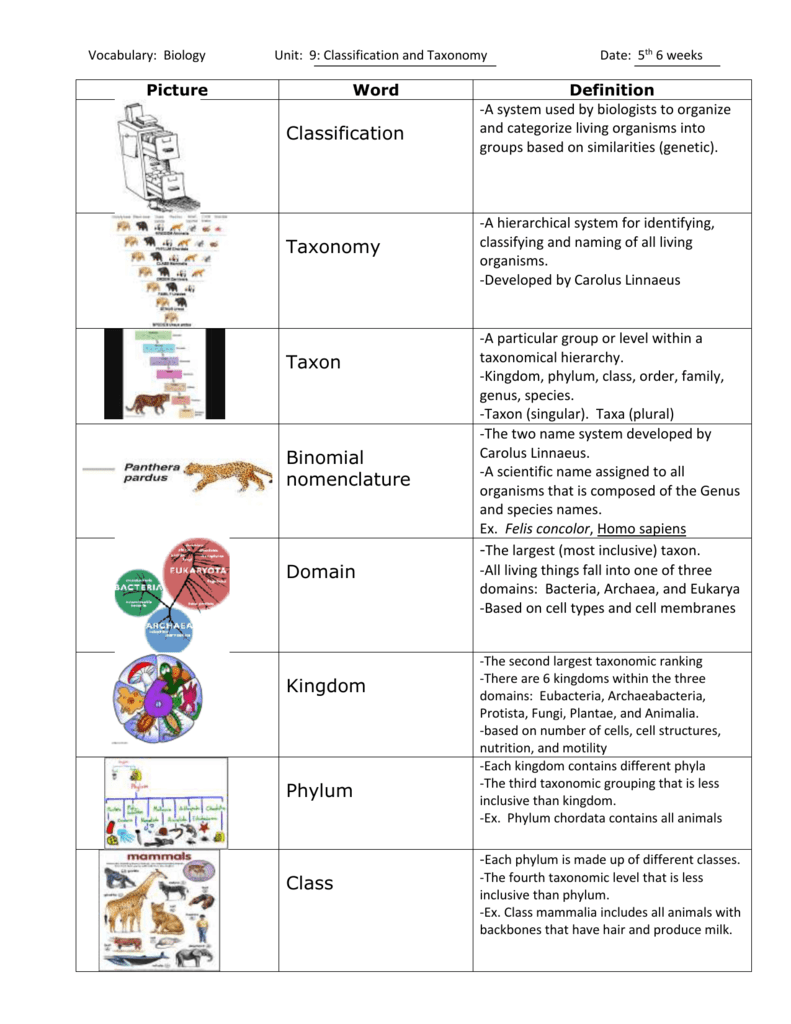
Each domain contains a collection of organisms with similar properties and evolutionary histories as scientists have organized them. The other two domains of life are archaea members of. Bacteria with a capital b refers to the domain bacteria one of the three domains of life.
Bacteria are single celled microorganisms with prokaryotic cells which are single cells that do not have organelles or a true nucleus and are less complex than eukaryotic cells. The domain bacteria comprises all organisms in the kingdom bacteria the domain archaea comprises the rest of the prokaryotes and the domain eukarya comprises all eukaryotes including organisms in the kingdoms animalia plantae fungi and protista. Free learning resources for students covering all major areas of biology.
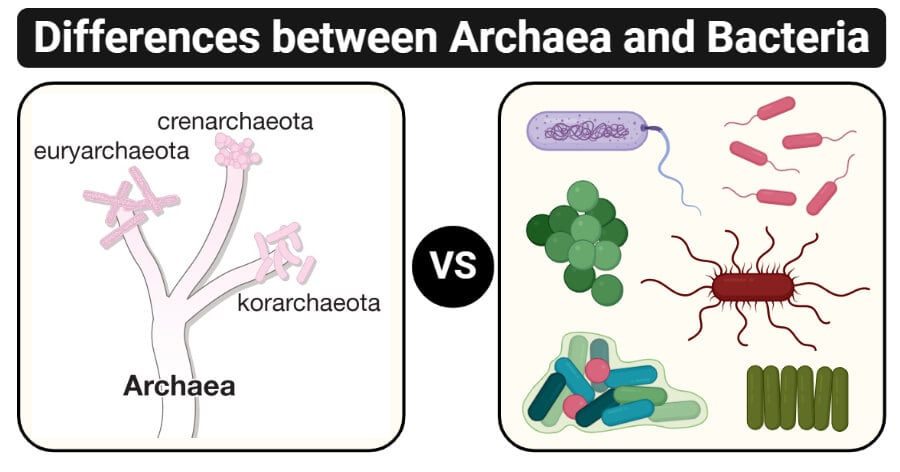
Bacteria even though bacteria are prokaryotic cells just like archaea their membranes are made of phospholipid bilayers. They characteristically do not have ether linkages like archaea and they are grouped into a different category and hence a different domain. Domains 1 taxonomy the highest taxonomic rank of organisms in which there are three groupings.