Transmembrane Domain Biology Definition

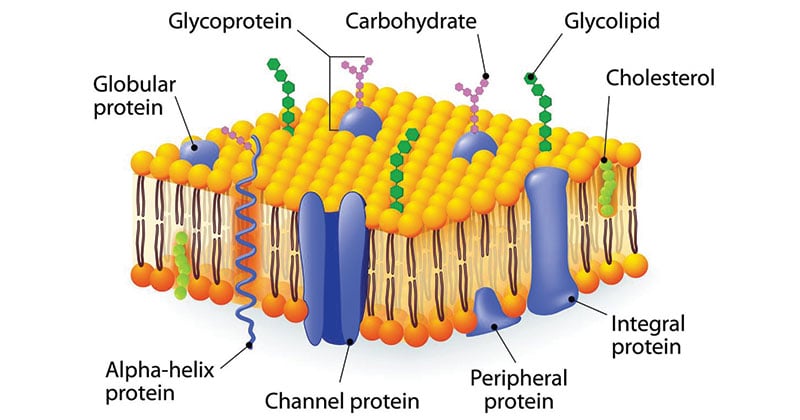
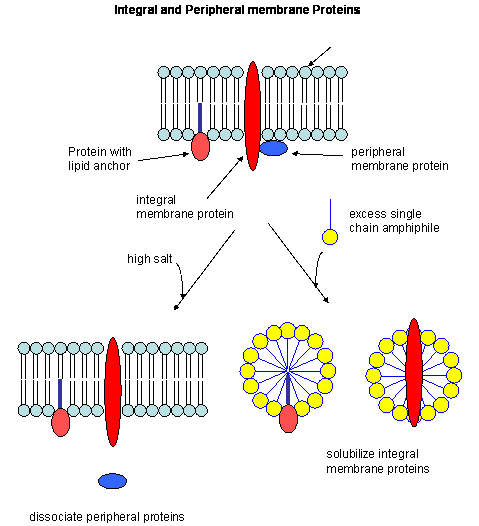
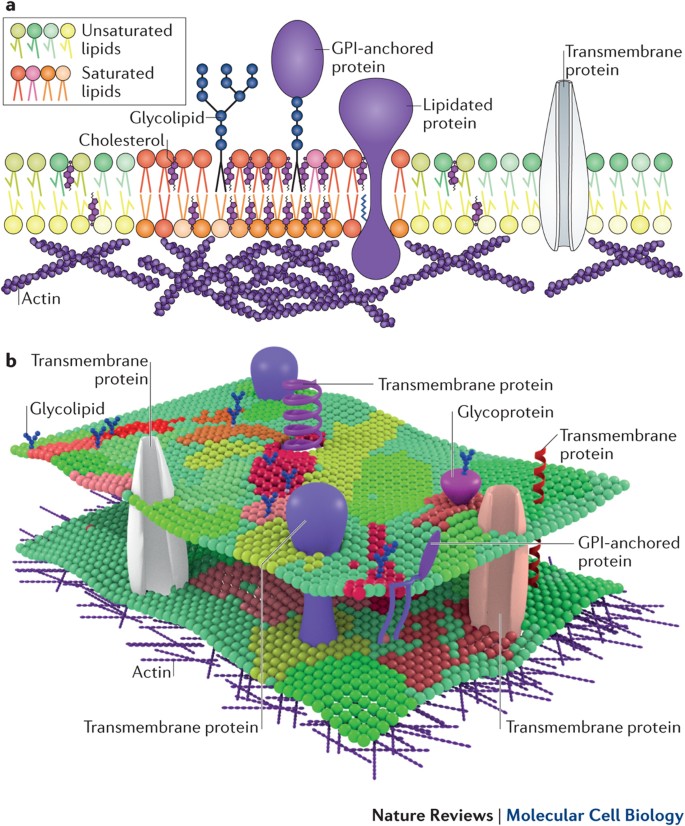
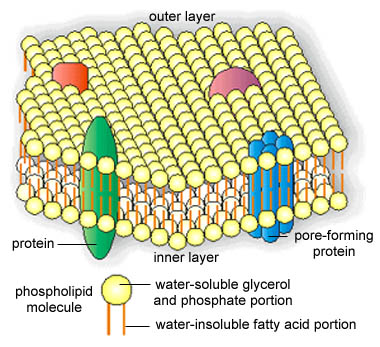
Transmembrane domains are regions of a protein that are hydrophobic so that they prefer to be inserted into the cell membrane such that the parts of the protein on either side of the domain are on opposite sides of the membrane.
Transmembrane domain biology definition. A comprehensive reference 2008. Biology any of three primary divisions of organisms consisting of the eukaryotes bacteria and archaea that rank above a kingdom in taxonomic systems based on similarities of dna sequences. Several public databases of dna sequences are available for analysis by any interested individual.
Each serves a specific function. Transmembrane in the largest biology dictionary online. Campbell biology by j b.
Law the land of one with paramount title and absolute ownership. Homologous unit of 110 120 amino acids groups of which make up the light and heavy chains of the immunoglobulin molecule. Amino acid stretches are called transmembrane domains.
If a transmembrane domain is found in a gene of unknown function it suggests that the encoded protein is located in the cellular membrane.